Benzene
Benzene is a colorless, fragrant, and volatile liquid with a yellow flame, along with the non-production of the industrial group. Use materials similar to polystyrene, synthetic rubber, and nylon. It is also widely used in the detergent and paint industries.
Each benzene molecule contains 6 carbon atoms and 6 hydrogen atoms in terms of the chemical classification of benzene belonging to the hydrocarbon family, which is a cyclic arrangement created as existing. This ring arrangement is called benzene, which is also present in most of the compounds, including aspirin, etc.
Adding benzene to gasoline increases its octane number and makes the engine run. For this reason, until the 1950s, most gasoline reduced benzene, but then tetra-ethyl lead became common in benzene. The obsolescence of leaded gasoline has led to the return of benzene to gasoline in some countries, but due to the negative effects of this substance on health due to the toxicity and carcinogenicity of this combination, there are free regulations that have been imposed on the amount of gasoline. Attention is reduced from one percent.
History of benzene
Benzene was first discovered by Michael Faraday in 1825. He separated benzene from a glowing compressed gas made from pyrolysis of whale oil, which he first called hydrogen bicarbonate. Then, in 1834, a man named Ail Hart Miterlish synthesized benzene by heating benzoic acid with calcium oxide, and by measuring its vapor density, it showed that benzene had the molecular formula C6H6. Today, benzene is extracted from large quantities of crude oil, but in the past, it was obtained by heating coal tar and then converting its vapor into liquid.
What is benzene-d6?
In general, to produce deuterium solvents such as benzene, etc., use the advantages of using non-deuterium molecules with heavy water in the presence of a suitable catalyst.
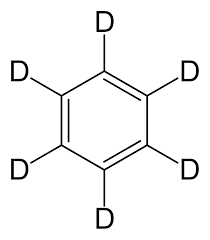
Deuterated benzene is a compound with the chemical formula (C6H6) in which the hydrogen atom ("H") is replaced by the isotope deuterium (heavy hydrogen) ("D"). D) It has a spin number of 0. If you reward hydrogen with deuterium, you can get a suitable, hassle-free solvent for NMR spectroscopy. Deuterated benzene is a common solvent used in NMR spectroscopy. Depending on the application and sensitivity of the NMR spectrometer, solvents with a degree of dotting between 98 99 and 99.96% are used. It should be noted that Moore's solvent may use the least amount of water possible because it specifies the minimum water with Carl Fisher and NMR.
The main applications of Deuterated benzene and its derivatives
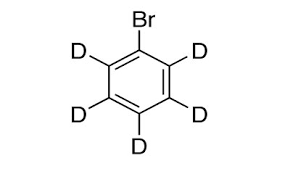
Deuterated benzene is used in the manufacture of electronic components because it has been proven to increase its power. Bromobenzene-d5 is used in the manufacture of electronic components and OLED displays. In addition, pharmaceutical companies and CMOs use bromobenzene-d5 to produce deuterated active drugs (API). A potential advantage for rewarding hydrogen atoms with deuterium atoms is that the combination of the two causes a pharmacokinetic effect that causes them to form and distribute in the body. This may reduce the number of doses needed by the patient compared to when non-prescription drugs are used.
Click to buy "deuterated benzene", "benzene-d6" ,"bromobenzen-d5" ,"Benzene-d6 ≥ 99.5 atom %D","benzene"
KEYWORD SECTION:
You can also find other articles about the above keywords in other languages with the use of these words.
benzene-d6 : In Chines: “苯-d6 “ , In Russian: бензол-d6
in Germany:Benzol-d6 in italian:benzene-d6