Introduction:
Newborn screening is a type of screening test that is done to detect abnormalities or congenital metabolic diseases early, in order to identify the disease at birth. Delayed diagnosis and treatment can lead to mental and physical problems, such as inability to move, mental retardation, malnutrition, inability to speak, Down syndrome and others. Factors such as the growing prevalence of neonatal diseases, government support for neonatal screening programs, and the growing neonatal population play a significant role in the market growth of this test. In addition, advances in infant screening technology are expected to drive market growth. However, the lack of proper healthcare infrastructure and trained professionals is likely to slow market growth somewhat.

What diseases are screened for?
1- Congenital hypothyroidism: This disease reduces the level of thyroid hormones and as a result causes severe physical and mental retardation. Early diagnosis and medical treatment will prevent any problems and the baby will continue to grow normally.
2. Phenylectonuria: Phenylalanine is one of the most important and essential amino acids in the body. The genetic defect of enzymes that cause the consumption of phenylalanine in the metabolic cycle increases its level in the body and its appearance in the urine. If left untreated, high levels of phenylalanine can damage brain tissue and lead to mental retardation. Early diagnosis and treatment with special diets help the baby grow normally.
3- Increased galactose (galactosemia): Children with this disease will not be able to use the sugar in milk (galactose) due to a genetic defect in the production of some enzymes. As a result, blood galactose is elevated and can cause cataracts and severe liver and brain damage. The first sign of this is prolonged and severe vomiting, and if left untreated, it can lead to very dangerous complications.
4 - congenital enlargement and overactive adrenal gland: In this disease, the body is unable to produce the hormone cortisol, and this deficiency causes physical and mental retardation, as well as the appearance of boyish traits in girls.
Favism: In this disease, one of the important enzymes of red blood cells is reduced and as a result, red blood cells are destroyed after consuming oxidants such as some drugs and beans. The patient quickly develops severe anaemia with shock, lethargy, and lethargy, and the disease in infants can prolong the course of jaundice.
5. Maple syrup disease: The cause of this disease is a congenital disorder in the absorption and use of several types of amino acids. As a result, the level of these amino acids in the blood increases and it smells like burnt sugar or maple sap gives body fluids, including urine. Accumulation of these amino acids leads to severe mental retardation and even death.
Advantages of newborn Screening
newborn screening is one of the great advances in child health in the last century and there have been many advances in the technologies used in neonatal screening. There are many benefits to screening your baby
Benefits such as:
Ability to diagnose multiple metabolic diseases in infant dried blood samples at birth
Low cost of diagnosis and prevention at birth, compared to the cost of treatment at older ages
Early treatment and intervention of at least 12,000 infants each year in the United States with genetic, hearing, and endocrine disorders
Contributing to the health of the community and ...
These same benefits have led governments to take effective action to raise awareness of newborn screening and its benefits. For example, increasing public sector funding for neonatal screening is mandatory in many US states, European countries, and many developed countries. In June 2018, the American Society of Hematology (ASH) launched a campaign to combat sickle cell disease in Africa and called on governments, especially in sub-Saharan Africa, to invest in neonatal screening. In addition, the US government implements programs such as the Quality Assurance Screening Program and the Inheritance Disorder Program at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) each year with the participation of various countries.
Therefore, such measures and programs by governments support market growth, and various governmental and non-governmental organizations are actively focusing on providing better options. One of the most important developments in this field is the commercialization of equipment used in this field. . Manufacturers have focused on sensitivity, clarity, operational power and cost-effectiveness to gain a foothold in the market.
Tandem mass spectrometry technology, meanwhile, has revolutionized the newborn screening market, reducing false-positive results and simplifying the screening process. These advances have led experts in the field to be optimistic that the health benefits of screening will increase in the future. All of these factors have led them to predict a growing market for newborn screening in the future.
newborn screening based on the technology used is divided into six sections:
Tandem Mass Spectrometry LC-MS / MS
DNA testing
Electrophoresis
Pulse oximetry
Enzyme-based assays
Hearing screening technology
is divided.
The LC-MS / MS department will play a significant role in advancing technology and raising awareness of neonatal disorders. Neonatal screening is also classified into four cases: dry blood smear test, vital congenital heart disease (CCHD) test, urine test, and hearing screening test. Dry bloodstain testing has received more attention due to its use in tandem mass spectrometry.
The use of this technique requires labelled compounds that are used as an internal standard in screening kits. In the following tables, you can see an example of these compounds:
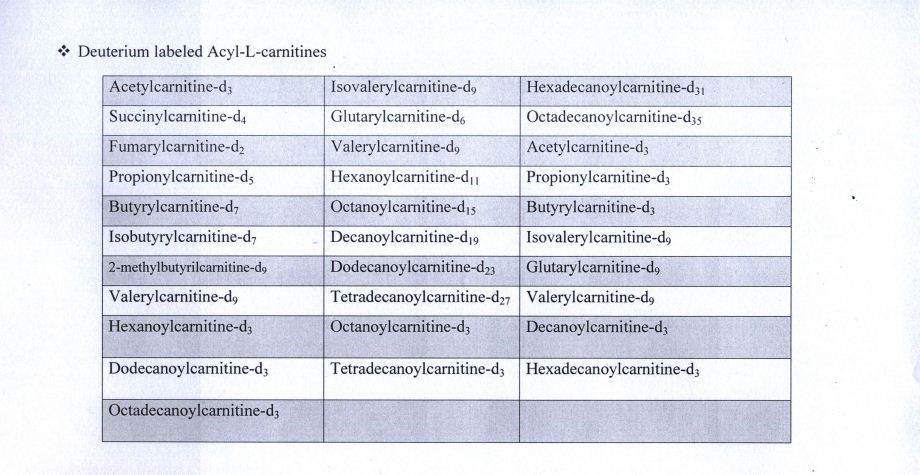
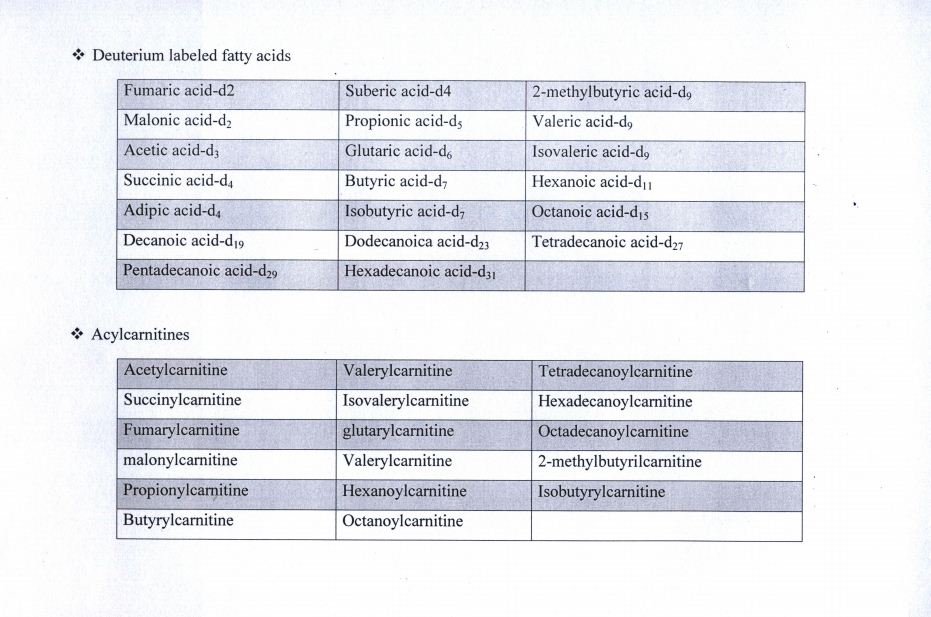
"LC-MS / MS" "newborn screening" "Internal standard" " deuterated compound in newborn screening"