Signal intensity in the 1H-NMR spectrum
Many modifications can be obtained from H-NMR. The first data is the amount of chemical displacement. With the help of this information, we determine the type of hydrogen atom that produces the signal. The second case is the surface ratios below the peaks. The area below the peak of an H-NMR is directly proportional to the number of hydrogen atoms produced.
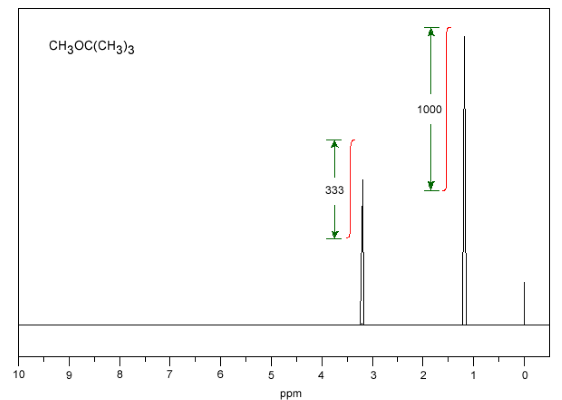
Today, this integration from the bottom of the chart is done by software, but in the past, it was displayed as a chart on the spectrum. In the image below, you can see the methyl tert-butyl ether spectrum.
In the image above, the integrals are shown in red. The ratio of these integrals is 333: 1000 or 1: 3. This spectrum shows that the left peak belongs to the oxygen-bound methyl group, which is also in line with our expectations because oxygen overlaps the hydrogen atoms. The peak on the right is 3 methyl groups in tert-butyl ether, which will have less decay due to the distance from the oxygen atom.
Spin spin splitting
In the image below, the peaks are seen as single or "single" and contain only one peak. However, in most cases, this does not happen. Peaks are split into several groups, mainly due to coupling between adjacent protons in the molecule.
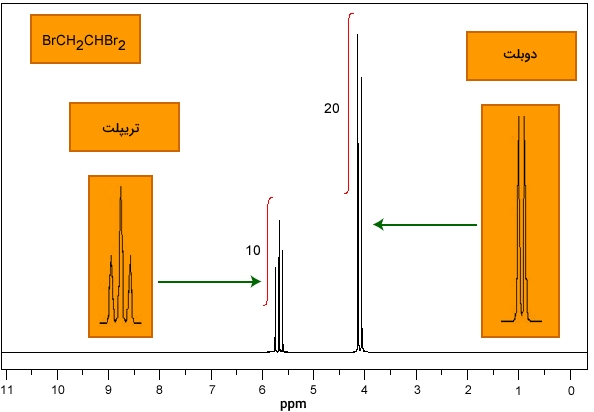
The magnetic resonance spectrum of the nucleus in the combinations of 1, 1, and 2-tri-bervotane is shown in the figure above. Note that the peaks are divided into two groups on the right and a triple on the left. In fact, we have the "Doublet" peak on the right and the "Triplet" peak on the left. The ratio of the level below the chart will be 1: 1 in the double peak and 1: 2: 1 in the triple peak.
The peak triplet corresponds to −CHBr2 − CHBr2 and the doublet corresponds to −CH2Br − CH2Br. "Spin-Spin Splitting" occurs between two specific types of hydrogen atoms on a carbon atom or adjacent carbon atoms. This is due to the interaction between the magnetic fields of one hydrogen atom and another. This interaction is important when the hydrogen atoms are chemically different.
Fixed coupling
Coupling Constant, denoted by the symbol J and the unit Hertz, is a measure of the interaction between a pair of protons.
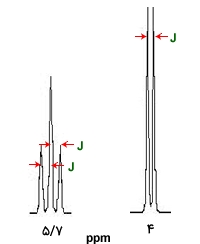
In an adjacent system, Ha – C – C – Hb, the coupling between HaHa and HbHb is denoted as JabJab. The coupling between HaHa and HbHb must be equivalent to the coupling between HbHb and HaHa, so we have:
Jab = JbaJab = Jba
The result of this equation is that the distances between the lines in the paired peaks must be equal to each other.
KEYWORD SECTION:
You can also find other articles about the above keywords in other languages with the use of these words.
Nuclear magnetic resonance: In Chines: “核磁共振 , In Russian: Ядерный магнитный резонанс” ؛IN Germany: “ Kernspinresonanz
Nuclear magnetic resonance applications: In Chines: 核磁共振应用
In Russian: Приложения ядерного магнитного резонанса
IN Germany: Kernspinresonanzanwendungen